What is an Autonomous Vehicle?
An autonomous vehicle is a car that can operate without the input of a driver. This can range from smaller assistive functions, such as cruise control and adaptive lane assistance, right down to fully automated, pilotless driving and navigation.
They sense their surroundings to navigate, detect changes in speed, traffic-flow, and environmental factors and dictate their route and functions accordingly. More advanced levels of autonomous driving systems allow vehicles to respond to unexpected hazards that a human driver would usually manage.
Over the last few years, autonomous car technology has advanced rapidly. Integrations are being regularly adapted to feature in modern cars and assist drivers in their day-to-day driving.
So, do autonomous vehicles have drivers?
There are many different levels of autonomous vehicles, some of which do not require the input of a driver. Though plenty of technology for fully autonomous vehicles exists, strict legislation and a lack of infrastructure makes it unlikely that we will see fully automated vehicles on public roads in the near future.
What are the 6 levels of driving automation?
Autonomous driving is determined by 6 levels of automation:
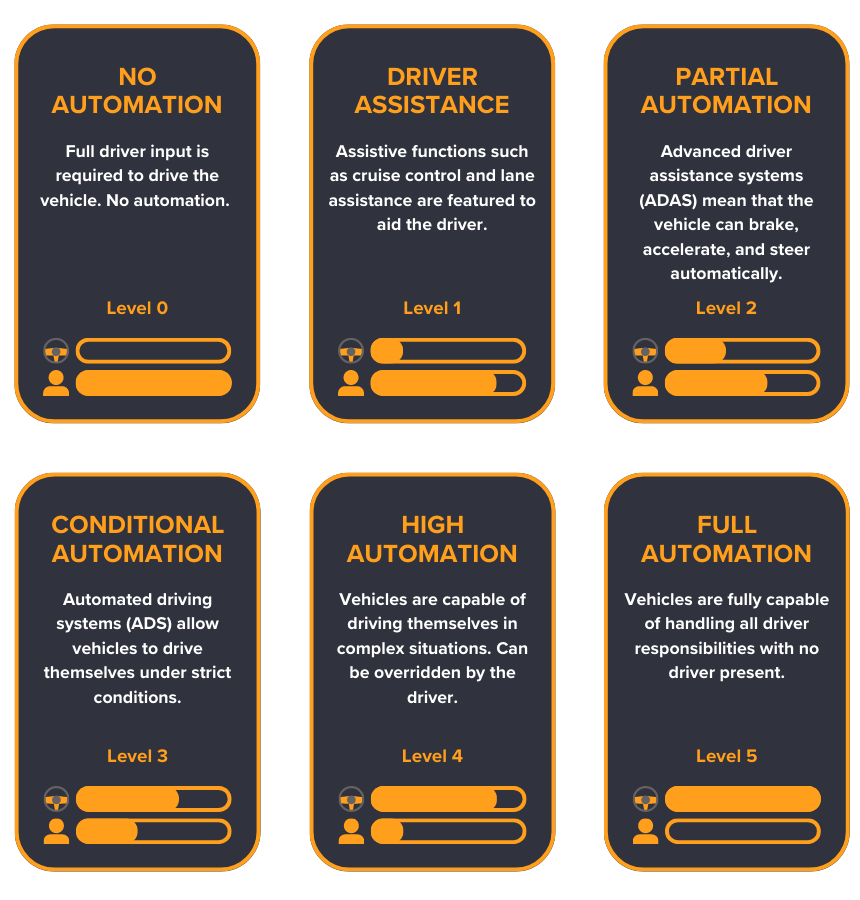
Level 0: No Automation. Full driver input is required to control the vehicle, including acceleration, braking, and steering. Most vehicles on the road today are level 0 automation.
Level 1: Driver Assistance. Some newer models of cars feature driving assistance controls, such as cruise control and lane assistance. These assist the driver, but do not take driving responsibility away from the driver.
Level 2: Partial Automation. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) are prominent. Cars can brake, accelerate, and steer automatically. The driver can still take full control of the vehicle, and must stay aware of potential hazards and traffic ahead of them.
Level 3: Conditional Automation. Level 3 features automated driving systems (ADS). Vehicles are able to drive themselves but only in certain conditions, such as long distance motorway driving. It is not necessary to keep both hands on the wheel at all times, but the driver must be ready to retake control at any given moment.
Level 4: High Automation. Level 4 cars are capable of driving themselves in complex situations without any input from the driver. They can still be manually overridden. Due to legislation and infrastructure, there are very few level 4 cars on the road.
Level 5: Full Automation. These cars are fully capable of handling all driver responsibilities. Thus, no driver is needed for a level 5 automated vehicle. It will be many years before we may see one on public roads.
What are the benefits of autonomous vehicles?
The future of self-driving cars is undeniably advancing, and has been evolving and adapting for many years. Instances of automated vehicle assistance have been featured since the early 1900s, where early cruise control innovations made a first appearance.
Many modern cars on the market are installed with modern automated technologies, such as SLI systems, and adaptive cruise control. What difference does this make for users on the road?
Improved Safety
At the forefront of modern automated vehicle technology are safety considerations aimed at reducing driving-related accidents and deaths. Features such as forward collision warning (FCW) systems and automatic emergency braking (AEB) are effective features that are designed to increase road safety for vehicle-users by reducing human error on the roads.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Modern autonomous vehicles are developed using extremely advanced engines that emit fewer emissions over their lifetime than conventional combustion engines. Automated vehicles also operate much more efficiently than non-automated vehicles, with less room for human-error and poor operational transmission performance.
Increased Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles require much less input from a human operator. This makes it more accessible to the elderly or those with disabilities, as operating the vehicle requires less physical and mental capabilities.
Data Collection
Installed with advanced computer systems, automated vehicles are able to communicate changes in traffic, congestion, and other environmental changes that will be useful for other users on the road. This data can be used by other vehicles and data systems to improve traffic infrastructures for the future.
Whilst there are still many challenges that autonomous vehicles face, new technological innovations are advancing at a rapid rate. We might be seeing autonomous vehicles on our roads in the future, but they still have a lot to go to ensure increased user safety.






